The Importance of Monitoring Grain Temperature in Farming
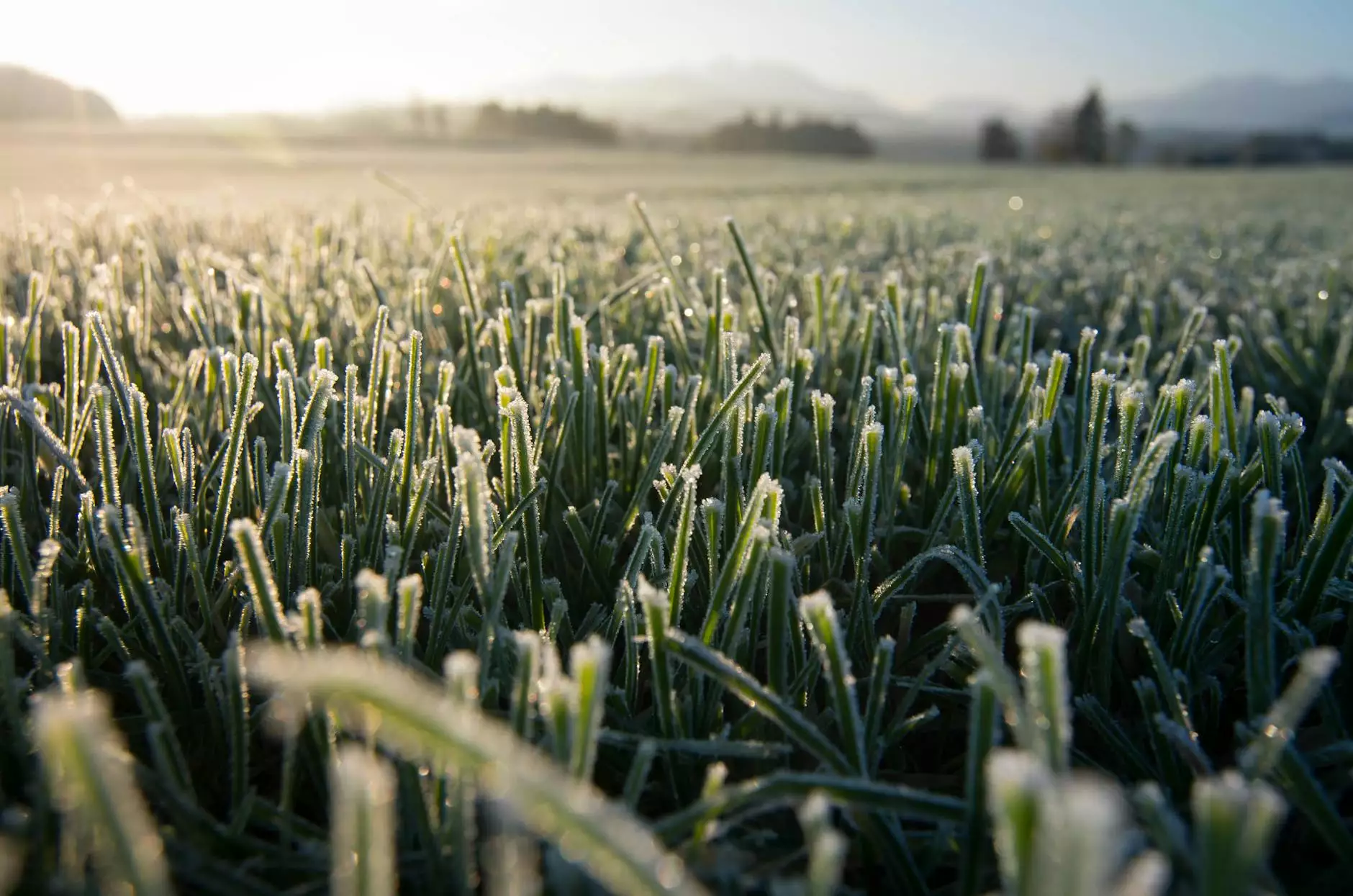

Grain temperature plays a crucial role in agriculture, particularly in the management and storage of grains. Farmers need to maintain optimal conditions for their crops not only to maximize yield but also to ensure the quality of the grain remains intact post-harvest. In this comprehensive article, we delve deep into the significance of monitoring grain temperature, the implications of not doing so, and practical solutions that farmers can incorporate to safeguard their harvest.
Understanding Grain Temperature
Grain temperature refers to the heat level of grains stored within bins or silos, and it is an important factor that influences quality and longevity. The ideal grain temperature varies depending on the type of grain, but generally, cooler temperatures help in preserving grain integrity.
The Science behind Grain Temperature
When grains are harvested, they contain moisture which can lead to various biological processes if not monitored. Microbial growth, insect infestations, and chemical changes are often a result of improper temperature control. Understanding the thermal dynamics involved in grain storage can enable farmers to implement better management strategies.
Why is Grain Temperature Important?
The impact of grain temperature can be broken down into several critical areas:
- Quality Preservation: Higher temperatures can lead to the degradation of essential grains, resulting in a loss of nutritional value and quality.
- Pest Control: Insects thrive in warm conditions. Keeping grain temperatures low can minimize pest infestations significantly.
- Moisture Management: Temperature influences moisture levels, which are crucial in preventing mold growth and other spoilage factors.
- Longevity of Storage: Proper grain temperature can extend the shelf life of stored grains, allowing for better planning and economic outcomes.
Effects of Inadequate Grain Temperature Control
Failing to maintain appropriate grain temperatures can result in devastating consequences for farmers. Some of the primary effects include:
1. Quality Degradation
As the grain temperature rises above the desired range, it can trigger undesirable chemical reactions such as lipid oxidation and protein denaturation. This can make grains less palatable and lower their market value.
2. Infestation Challenges
Insects such as weevils and other pests become problematic at higher temperatures, threatening the entire grain inventory. Maintaining lower temperatures can serve as a natural pest deterrent.
3. Increased Spoilage and Loss
Microbial activities flourish at elevated temperatures, leading to potential spoilage. Mold and other fungi can develop quickly, resulting in significant financial losses.
4. Safety Hazards
The risks don't end with loss of quality; high grain temperature can also lead to safety issues involving spontaneous combustion, which can jeopardize the entire grain store as well as the safety of workers.
How to Monitor and Control Grain Temperature
Effective grain temperature management is essential for successful farming. Here are some practical strategies:
1. Utilize Temperature Monitoring Systems
Investing in a robust grain temperature monitoring system can provide real-time data. These systems often include:
- Digital sensors: These can be placed throughout grain storage to track temperature variations.
- Remote Monitoring Tools: Systems equipped with IoT capabilities allow farmers to access data from anywhere, facilitating quicker decision-making.
2. Regular Inspections
Scheduled inspections of grain storage facilities are vital. Farmers should check the grain temperature using infrared thermometers or manual temperature probes to ensure readings fall within the ideal range.
3. Improve Airflow in Storage
Proper ventilation is crucial. Ensuring that air can circulate through stored grain helps to regulate temperature and moisture levels, preventing spoilage.
4. Cooling Techniques
In climates that are prone to heat, cooling techniques can be beneficial:
- Fans: Installing fans in storage bins can promote airflow and lower temperatures.
- Hallway Systems: Constructing a cooling hallway can provide a section within storage areas that maintains a cooler temperature.
Working with Farm Equipment: Repair and Maintenance
When managing grain temperatures, the equipment used in farming plays a vital role. Regular farm equipment repair ensures that all machinery functions correctly, particularly during crucial periods such as harvest time. Understanding the importance of reliable farming equipment highlights how it contributes to effective grain temperature management.
Investing in Quality Farming Equipment
Farmers should purchase and maintain quality farming equipment to avoid issues that can jeopardize grain storage conditions. Some essential tools include:
- Grain Bins: Ensure that the bins used are designed for insulation and temperature regulation.
- Harvesters: Harvesters equipped with moisture management systems can help ensure that grains are stored at optimal moisture content right from the start.
The Role of TSGC Inc. in Grain Temperature Management
Businesses like TSGC Inc. offer exceptional services in farming equipment and its repair. Their expertise can ensure that all machinery operates effectively, aiding in the overall grain temperature management processes. Regular repairs and updates to farming equipment help in achieving the best results in grain storage and temperature control.
Conclusion: The Future of Grain Temperature Management
As the agricultural sector continually evolves, the need for innovative solutions for managing grain temperature becomes even more critical. By implementing technology, regular inspections, and quality equipment, farmers can protect their investments while ensuring optimal crop yield and quality.
Embracing best practices will enhance your operational efficiency and ultimately result in higher profits. Being vigilant about grain temperature management is not merely a suggestion; it is essential for survival and success in the agriculture industry. The future of farming lies in our ability to adapt and evolve, ensuring that practices concerning grain temperature monitoring and management remain a top priority. Farmers must think proactively to safeguard their crops and achieve fulfilling success with their harvests.